科学支持
ACADEMIC PAPER
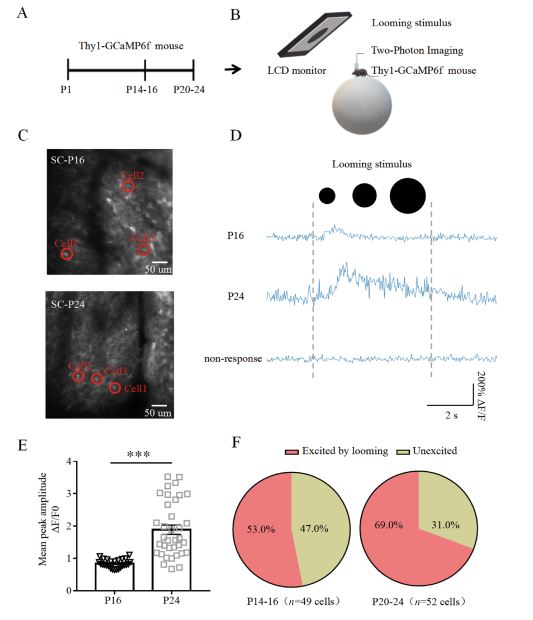
Environmental threats often trigger innate defensive responses in mammals. However, the gradual development of functional properties of these responses during the postnatal development stage remains unclear. Here, we report that looming stimulation in mice evoked flight behavior commencing at P14-16 and had fully developed by P20-24. The visual-evoked innate defensive response was not significantly altered by sensory deprivation at an early postnatal stage. Furthermore, the percentages of wide-field and horizontal cells in the superior colliculus were notably elevated at P20-24. Our findings define a developmental time window for the formation of the visual innate defense response during the early postnatal period and provide important insight into the underlying mechanism.
First published: 2022 Jul
more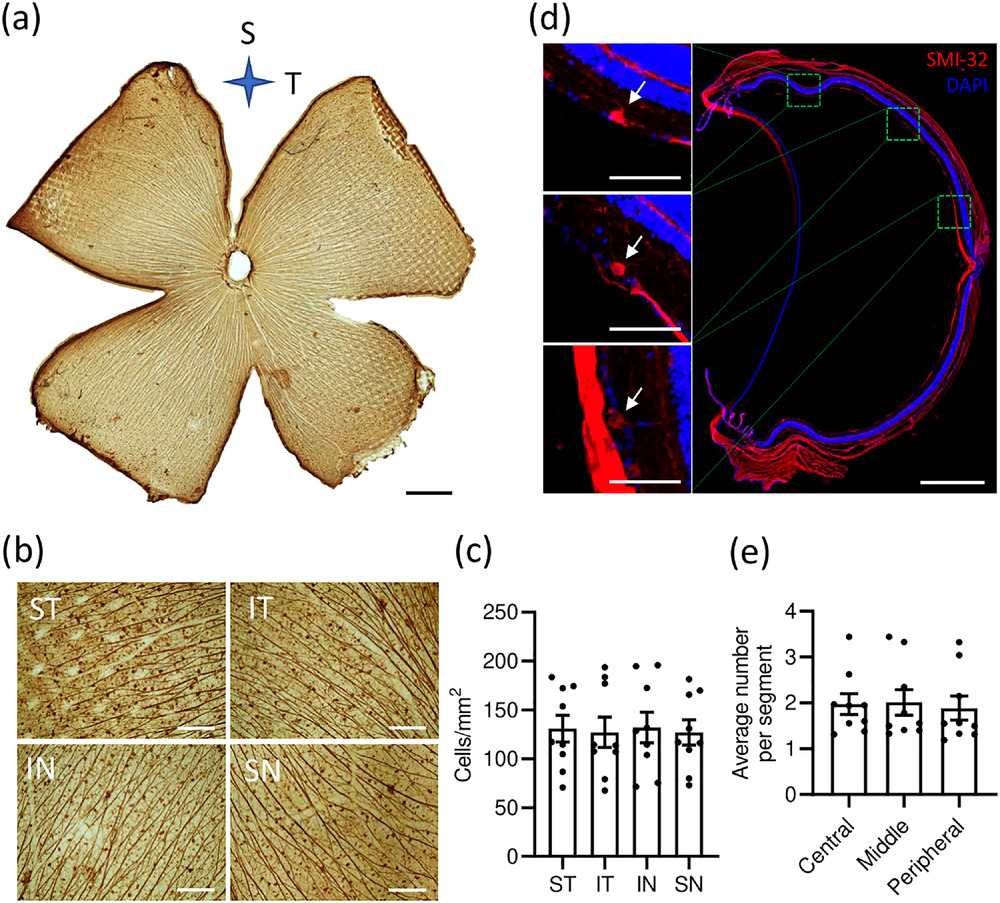
SMI-32 is widely used to identify entire populations of alpha retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), and several SMI-32+ RGC subsets have been studied thoroughly in rodents. However, due to the thick cover of SMI-32+ neurofilaments, the morphology of SMI-32+ RGCs in the central retinal region is obscured and rarely described. Moreover, SMI-32 labels more than one morphological RGC type and the full morphological characteristics and distribution of SMI-32+ RGCs have yet to be discovered. Here, using intracellular neurobiotin injections combined with SMI-32 antibody staining, we investigated morphological and distributional properties of the entire SMI-32+ RGCs population in the rat retina. We found that SMI-32+ RGCs were evenly distributed throughout the rat retina. We compared the morphological features of SMI-32+ ON and OFF cells in the central, middle, and peripheral retinal regions. We found that SMI-32+ RGCs in different regions have distinct characteristics, such as the soma area and the dendritic field area, and Sholl analysis of ON cells and OFF cells revealed significant differences between each region. We classified SMI-32+ RGCs into five clusters based on morphological features and found that a majority of SMI-32+ RGCs belong to alpha-like cells; however, a small proportion of SMI-32+ RGCs had small soma and small dendritic fields. Together, we present a full description of the morphology and distribution of SMI-32 immunoreactive RGCs in the rat retina.
First published: 21 November 2021
more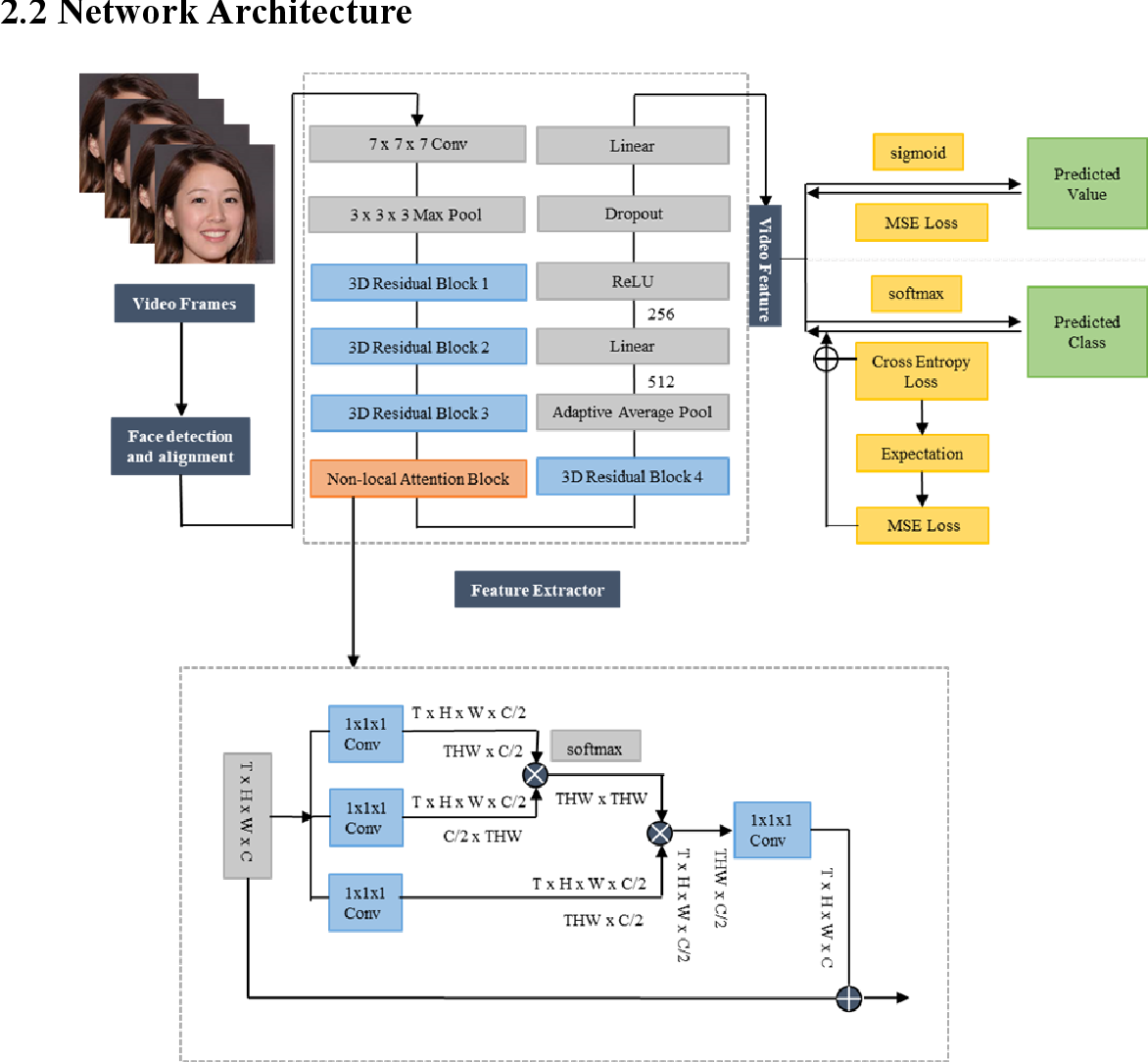
Fatigue detection is valued for people to keep mental health and prevent safety accidents. However, detecting facial fatigue, especially mild fatigue in the real world via machine vision is still a challenging issue due to lack of non-lab dataset and well-defined algorithms. In order to improve the detection capability on facial fatigue that can be used widely in daily life, this paper provided an audiovisual dataset named DLFD (daily-life fatigue dataset) which reflected people's facial fatigue state in the wild. A framework using 3D-ResNet along with non-local attention mechanism was training for extraction of local and long-range features in spatial and temporal dimensions. Then, a compacted loss function combining mean squared error and cross-entropy was designed to predict both continuous and categorical fatigue degrees. Our proposed framework has reached an average accuracy of 90.8% on validation set and 72.5% on test set for binary classification, standing a good position compared to other state-of-the-art methods. The analysis of feature map visualization revealed that our framework captured facial dynamics and attempted to build a connection with fatigue state. Our experimental results in multiple metrics proved that our framework captured some typical, micro and dynamic facial features along spatiotemporal dimensions, contributing to the mild fatigue detection in the wild.
First published: April 2021
more
Real-time ocular responses are tightly associated with emotional and cognitive processing within the central nervous system. Patterns seen in saccades, pupillary responses, and spontaneous blinking, as well as retinal microvasculature and morphology visualized via office-based ophthalmic imaging, are potential biomarkers for the screening and evaluation of cognitive and psychiatric disorders. In this review, we outline multiple techniques in which ocular assessments may serve as a non-invasive approach for the early detections of various brain disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), Alzheimer's disease (AD), schizophrenia (SZ), and major depressive disorder (MDD). In addition, rapid advances in artificial intelligence (AI) present a growing opportunity to use machine learning-based AI, especially computer vision (CV) with deep-learning neural networks, to shed new light on the field of cognitive neuroscience, which is most likely to lead to novel evaluations and interventions for brain disorders. Hence, we highlight the potential of using AI to evaluate brain disorders based primarily on ocular features.
First published: 21 April 2021
more
Patients with Bipolar Disorder (BD) are associated with aberrant uncinate fasciculus (UF) that connects amygdala-ventral prefrontal cortex (vPFC) system, but the casual relationship is still uncertain. The research aimed to investigate the integrity of UF among offspring of patients with BD and investigate its potential causal association with subsequent declaration of BD. The fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) of UF were compared in asymptomatic offspring (AO, n = 46) and symptomatic offspring (SO, n = 45) with a parent with BD, and age-matched healthy controls (HCs, n = 35). Logistic regressions were performed to assess the predictive effect of UF integrity on the onset of BD. The three groups did not differ at baseline in terms of FA and MD of the UF. Nine out of 45 SO developed BD over a follow-up period of 6 years, and the right UF FA predicted the onset of BD (p = 0.038, OR = 0.212, 95% CI = 0.049-0.917). The ROC curve revealed that the right UF FA predicted BD onset (area-under-curve = 0.859) with sensitivity of 88.9% and specificity of 77.3%. The complementary whole-brain tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) showed that widespread increases of FA were found in the SO group compared with HCs, but were not associated with the onset of BD. Our data provide evidence supporting the causal relationship between the white matter structural integrity of the amygdala-vPFC system and the onset of BD in genetically at-risk offspring of BD patients.
First published: 2021 Feb 5
more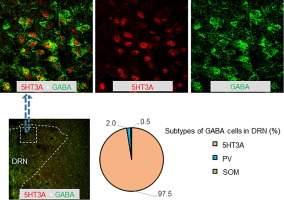
The dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) participates in stress responses and in mood regulation via its ascending release of serotonin (5-HT) onto neural circuits within the forebrain. Although the 5-HT DRN region is easily defined via 5-HT-expressing DRN neurons, the neuroarchitecture and microcircuitry that confer its multifunctionality have remained incompletely understood and have required further investigation. In this present study, neurochemical interactions within different subregions of the rat DRN were precisely analyzed. We found that 97.5% of GABAergic neurons in the DRN expressed ionotropic 5-HT3A receptors (5-HT3ARs), whereas there were only rare parvalbumin (PV)-positive or somatostatin (SOM)-positive GABAergic neurons. Furthermore, corticosterone administration into male rats as a rodent model of depression induced significantly higher c-Fos expression in 5-HT3AR-positive GABAergic neurons compared to that in 5-HT neurons within the DRN. Taken together, our findings suggest that 5-HT3AR-positive GABAergic neurons in the DRN participate in responses to stress hormones in a rat model of depression.
First published: 10 August 2020
more
The COVID-19 disease has resulted in an unprecedented shutdown in many cities and regions in China (1). In addition to concerns raised about the transmission of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), health care providers are also subject to isolation in and deployment to areas where the infection is epidemic. Reports of deaths of health care providers due to SARS-CoV-2 not only reflect the seriousness of the infection but also add to greater distress and burden, disproportionately on health care providers. Taken together, the health, well-being, and functioning of health care providers in China providing assistance to individuals affected by SARS-CoV-2 are at risk. Herein, we sought to evaluate measures of depression, anxiety, insomnia, and distress among health care providers providing care for individuals affected by SARS-CoV-2.
First published: 2020 Jul 1
more
Aerobic exercise impacts the anterior cingulate cortex in adolescents with subthreshold mood syndromes: a randomized controlled trial study
First published: 2020 May 18
more
Neuro-inflammation might impact on clinical manifestations and cognition function via changing the volumes of key brain structures such as the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) in bipolar disorder (BD). In this study, we investigated the interrelations among interleukin (IL)-6 cytokine level, grey matter (GM) volume of the anterior cingulated cortex (ACC), and attention function among offspring of parents diagnosed with BD. The offspring were categorized as being either asymptomatic or symptomatic based on whether they manifested pre-defined sub-threshold mood symptoms. We found that the symptomatic offspring showed significantly higher serum levels of IL-6 than the asymptomatic offspring (F(1, 59) = 67.65, p < 0.001). On the brain level, we obtained significant interactive effect of group and IL6 level on the ACC GM (PFWE = 0.017). Specifically, the GM volume of the rostral ACC was negatively associated with the levels of IL-6 in the asymptomatic offspring (PFWE = 0.021), but not the symptomatic offspring (PFWE > 0.05). Mediation analyses revealed that the GM volume of the rostral ACC significantly mediated the negative association between the IL-6 levels and attention performance in the asymptomatic offspring (bootstrapping Confidence Interval (CI) = -6.0432 to -0.0731) but not the symptomatic offspring (bootstrapping CI = -0.3197 to 1.3423). Our data suggest that the asymptomatic and symptomatic bipolar offspring may exhibit different neurocognitive-inflammatory profiles, which could be further validated as viable biosignatures for BD risk and resilience.
First published: 2020 Jan
more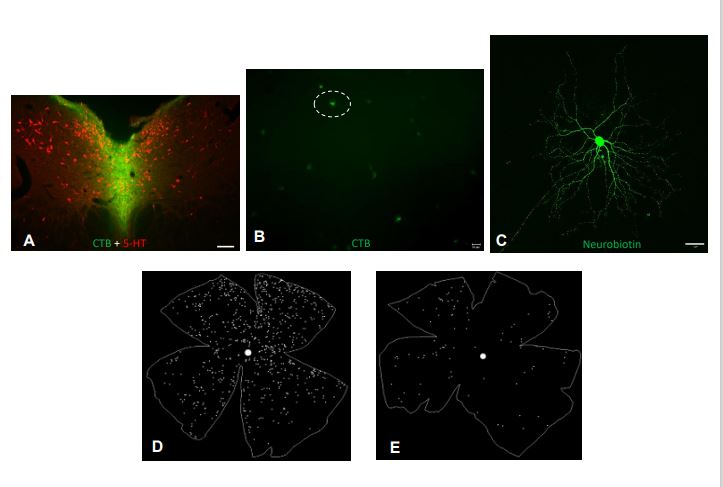
Background Light therapy is frequently demonstrated by clinical trials to be effective to seasonal or non-seasonal major depression. However, the pathway underlying the light effect on mood remains unclear. Since a retino-raphe pathway was previously indicated to modulate 5-HT production, we hypothesize that the retinal projection into dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) may play an important role in the light therapy for depression. Methods A rat model of 14-day corticosterone administration (40 mg/kg/day subcutaneous injection) was mainly used to test the effect of light therapy on non-seasonal depressant-like behavior, and the involved neural circuitry and neurochemistry as well. Results Behavior results revealed that the bright light therapy especially with the blue light of 470 nm and 400 lux, effectively reversed the depression-like responses in those stressed rats. After elimination of retino-raphe projection using immunotoxin (Saporin) the effect of light therapy was significantly attenuated. Whereas activation of retino-raphe projection using HM3q chemogenetics was shown an effect similar to fluoxetine treatment. Furthermore, 5-HT3A positive GABA cells in the DRN were activated with high c-Fos expression that involved in an inhibition of 5-HT synthesis and a subsequent depressive behavior. While light therapy through retino-raphe projection deactivated the hyperaction of those GABA cells in the DRN; that eventually contributed to the antidepressant effect from light therapy. Conclusions Our results indicate that the retino-raphe circuitry engaged antidepressant effect in DRN that contributed to the light therapy to the non-seasonal depression. 5-HT3A positive GABA cells in DRN was indicated to mediate this function of retino-raphe projection.
First published: 29 October 2019
more
Aberrant structural (diffusion tensor imaging [DTI]) and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imagining connectivity are core features of bipolar disorder. However, few studies have explored the integrity agreement between structural and functional connectivity (SC-FC) in bipolar disorder. We examine SC connectivity coupling index whether could potentially provide additional clinical predictive value for bipolar disorder spectrum disorders besides the intramodality network measures. By examining the structural (DTI) and resting-state functional network properties, as well as their coupling index, among 57 euthymic bipolar disorder patients (age 13-28 years, 18 females) and 42 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (age 13-28 years, 16 females), we found that compared to controls, bipolar disorder patients showed increased structural rich-club connectivity as well as decreased functional modularity. Importantly, the coupling strength between structural and functional connectome was decreased in patients compared to controls, which emerged as the most powerful feature discriminating the two groups. Our findings suggest that structural-functional coupling strength could serve as a valuable biological trait-like feature for bipolar disorder over and above the intramodality network measures. Such measure can have important clinical implications for early identification of bipolar disorder individuals, and inform strategies for prevention of bipolar disorder onset and relapse.
First published: 2019 Aug 15
more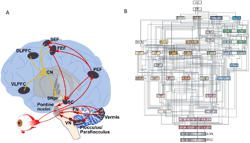
Here we summarize abundant excuses that support the eye detection can be as a noninvasive approach to early diagnose some brain disorders, including Alzheimer disease (AD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), schizophrenia (SZ) and major depressive disorder (MDD). Real-time ocular responses in everyone are tightly associated with emotional state and cognitive processing in the brain. At the eyeball areas, at least changes involved saccades, pupil response, blinking, microvascular network morphology and thickness of retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) are potentially to be candidates of biomarker to screen and evaluate brain disorders. These days medical big data will be more accessible especially with the help of advanced artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze precisely. Computer vision combined with machine-learning based AI particularly deep-learning neural networks sheds a new light on cognitive neuroscience, and many patients with psychotic disorders will primarily benefit from this interdisciplinary advance to induce self-evaluation and real-time intervention on brain disorders. Finally, we call for more AI applications going to approach brain disorder issues, meanwhile, AI technology used in brain healthcare should be working together with biological intelligence as we are running an AI manifestation for major depression
First published: 22 February 2019
more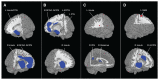
Current knowledge on objective and specific neural markers for bipolar risk and resilience-related processes is lacking, partly due to not subdividing high-risk individuals manifesting different levels of subclinical symptoms who possibly possess different levels of resilience.
First published: 2018 Oct 1
more
Observations from clinical trials have frequently demonstrated that light therapy can be an effective therapy for seasonal and non-seasonal major depression. Despite the fact that light therapy is known to have several advantages over antidepressant drugs like a low cost, minimal side-effects, and fast onset of therapeutic effect, the mechanism underlying light therapy remains unclear. So far, it is known that light therapy modulates mood states and cognitive functions, involving circadian and non-circadian pathways from retinas into brain. In this review, we discuss the therapeutic effect of light on major depression and its relationship to direct retinal projections in the brain. We finally emphasize the function of the retino-raphe projection in modulating serotonin activity, which probably underlies the antidepressant effect of light therapy for depression.Despite the fact that light therapy is known to have several advantages over antidepressant drugs like a low cost, minimal side-effects, and fast onset of therapeutic effect, the mechanism underlying light therapy remains unclear. So far, it is known that light therapy modulates mood states and cognitive functions, involving circadian and non-circadian pathways from retinas into brain. In this review, we discuss the therapeutic effect of light on major depression and its relationship to direct retinal projections in the brain. We finally emphasize the function of the retino-raphe projection in modulating serotonin activity, which probably underlies the antidepressant effect of light therapy for depression.
First published: 2018 Apr
more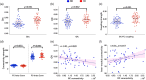
To compare frontal-striatal brain volumes between offspring of individuals with bipolar disorder (BD) and healthy controls; to investigate the associations of body mass index (BMI) and age with brain volumes; and to assess the moderating effects of BMI and age on the relationship between risk status and structural brain differences.
First published: 2018 Feb
more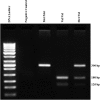
To compare brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels between offspring of individuals with bipolar disorders (BD) and healthy controls (HCs) and investigate the effects of BDNF levels and body mass index (BMI) on brain structures.
First published: 2017 Dec
more
Rejection sensitivity is a personality disposition characterized by oversensitivity to social rejection. Using a three-level meta-analytic model, 75 studies were reviewed that examined associations between rejection sensitivity and five mental health outcomes: depression, anxiety, loneliness, borderline personality disorder, and body dysmorphic disorder. The results showed significant and moderate associations between rejection sensitivity and depression (pooled r=0.332; p<0.001), anxiety (pooled r=0.407; p<0.001), loneliness (pooled r=0.386; p<0.001), borderline personality disorder (pooled r=0.413; p<0.001), and body dysmorphic disorder (pooled r=0.428; p<0.001). The associations between rejection sensitivity and depression, anxiety, and borderline personality disorder varied by type of sample, but the associations were similar for clinical and non-clinical (i.e., community) samples. The association between rejection sensitivity and anxiety was negatively moderated by percentage of females in samples. The association between rejection sensitivity and depression was negatively moderated by length of follow-up. The longitudinal associations between rejection sensitivity and depression, anxiety, and loneliness were stable over time. Implications of the findings for both risk assessment and prevention and intervention strategies in mental health practice are discussed.
First published: 2017 Nov
more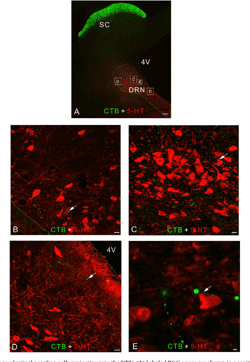
A retinal projection into the dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN), namely, the retino-raphe projection, exists in many species. The rat is one of several species in which a retino-raphe projection has been described; however, the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) types that contribute to this pathway are unknown.
First published: 1 December 2015
more
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) have demonstrated their potentials as medical implant biomaterials. Neural stem cells (NSCs) grown on/in PHA scaffolds may be useful for repairing central nervous system (CNS) injury. To investigate this possibility, nanofiber matrices (scaffolds) prepared from several PHA via a novel phase separation process were studied to mimic natural extracellular matrix (ECM), and rat-derived NSCs grown in the PHA matrices were characterized regarding their in vitro differentiation behaviors. All three PHA materials including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB), copolymer of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 4-hydroxybutyrate (P3HB4HB), and copolymer of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 3-hydroxyhexanoate (PHBHHx) supported NSC growth and differentiation both on their 2D films and 3D matrices. Among three PHA nanofiber matrices, PHBHHx one showed the strongest potentials to promote NSC differentiation into neurons which is beneficial for CNS repair. Compared to the 2D films, 3D nanofiber matrices appeared to be more suitable for NSC attachment, synaptic outgrowth and synaptogenesis. It was suggested that PHBHHx nanofiber scaffolds (matrices) that promote NSC growth and differentiation, can be developed for treating central nervous system injury.
First published: 1 May 2010
morePATENTS
POPULAR SCIENCE

“正常”,其实是另一种偏见
“在十九世纪之初,“正常”(normal)这个英文单词完全不用来形容人。它是一个数学术语,意为直角。” 当数学上的“离中性”被强加“离经叛道”的社会评价,人们开始用对所谓“正常”的迷恋,来规避“独立思考”和“特立独行”带来的风险。

【转载】苹果封神头显Vision Pro竟暗藏「脑机接口」!苹果前员工疯狂揭秘读心操控
苹果Vision Pro的横空出世,一夜之间在全球引起轩然大波。正如库克所称,这将开启「空间计算」时代,足见Vision Pro对所有人来说意义非凡。戴上Vision Pro,只需眨眨眼,捏合手指,甚至动动嘴,「头号玩家」的科幻便成为可能。
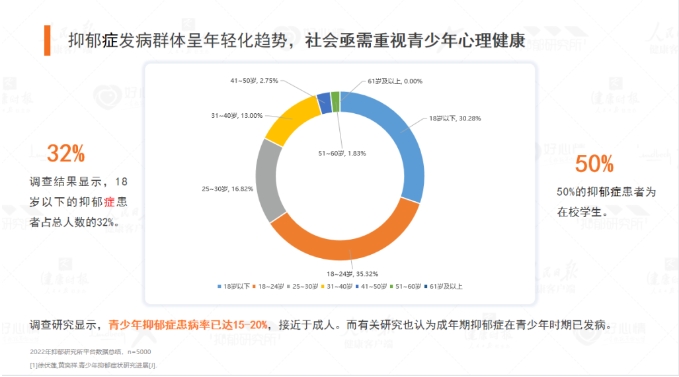
《2022国民抑郁症蓝皮书》发布,抑郁症患者中50%为在校生
6月29日,人民日报健康客户端、健康时报、好心情心理医疗和心理健康数字服务平台抑郁研究所等,共同发布《2022国民抑郁症蓝皮书》。蓝皮书通过用户调研、文献研究、专家评定分析等方法,汇聚分析大量数据,聚焦国民抑郁症现状、抑郁症患者现状、患者就医现状、患者用药现状、预防与干预5大方面,呼吁国民重视心理健康,探讨新兴诊疗模

五大看点 领略“心理服务机构精准发展”
7月16日-17日,由中国心理学会心理服务机构工作委员会、教育部人文社科重点研究基地天津师范大学心理与行为研究院、国民心理健康评估与促进协同创新中心主办,延续往期六届高峰论坛步履,第七届全国心理服务机构发展模式高峰论坛以心理服务·精准发展为主题开展。

安眠药能帮你睡个好觉吗?这篇文章让你一次看透睡眠药物治疗!
根据权威调查,失眠已经是40%中国人的老朋友了。虽然失眠不属于严重疾病,但失眠会严重妨碍人的工作、学习、日常生活,长期失眠还会造成更大影响,严重影响人的身心健康。这篇文章帮你一次看清失眠的第一线疗法--睡眠药物治疗,致力于助你夜夜好眠!

布局元宇宙中的平行世界:从facebook改名meta说起
美东时间2021年10月28日,扎克伯格在Connect大会上正式宣布将“Facebook”更名为“Meta”——元宇宙(MetaVerse)的前缀。“Meta”源于希腊语,意为“超越”或“之上”;元宇宙,可以理解为宇宙之外的超现实世界,恰好呼应了本次大会的主题——AR与VR(增强现实与虚拟现实)。

短视频成瘾背后的原理你知道吗?
抖音、快手、美拍、秒拍、小咖秀……短视频行业的市场规模逐渐接近2000亿,并占据了用户使用时长排行榜第一名。智能算法的出现让短视频行业在2017年时进入了惊人的爆发期,而在去年,新冠疫情导致的隔离又再次促进了其用户规模的大幅增长。
游戏治愈大脑:“游戏化时代”的处方药
020年6月15日,美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准了有史以来第一款视频游戏(美国Akili Interactive公司研发的EndeavorRx)作为疾病治疗(儿童多动症,ADHD)的处方药。
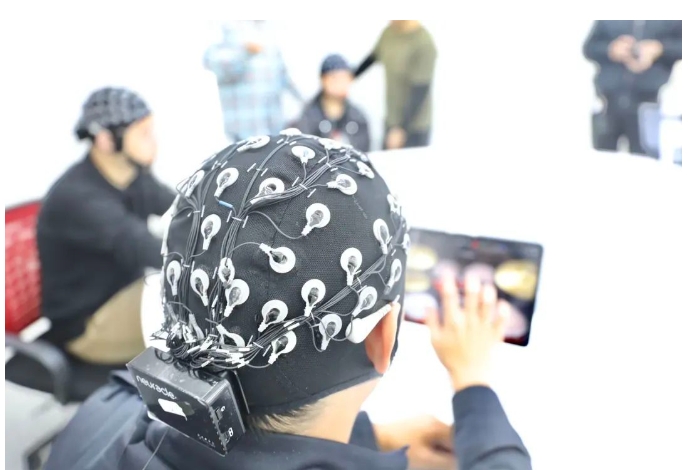

打游戏治病好不好?陈天桥雒芊芊研究院首个脑科学前沿实验室在华山医院投用
“除了药片、手术刀等,我们对治疗手段的认识要更开阔些,未来,认知障碍老人未必要吃药,可以每天打一段时间的游戏,延缓认知衰退。‘数字医学’带来的前沿疗法将超越现有我们眼睛看得见的药片。”

重磅!李飞飞入选美国国家医学科学院,她用AI改变了医疗
10月19日,美国国家医学科学院(National Academy of Medicine)在年度会议上宣布选举90名正式成员和10名国际成员。在正式成员名单中,「华人AI女神」李飞飞入选,她本人也发推表达谢意,并表示「希望人工智能能够通过改善医疗服务来帮助我们的临床医生和患者。」

英国记者揭露药物骗局:50%患者服药无效,2/3症状未缓解!
“我有抑郁症,所以就去死一死,没什么重要的原因,大家不必在意我的离开。拜拜啦。” 这是一条来自网友“走饭”的微博消息。它的主人是位普通的90后女孩,因为身患抑郁症,在2012年3月17日的凌晨上吊自杀。

看完这篇影评,才算真正看完《头脑特工队》
为什么我们在面对一个人时心里会问:TA到底在想什么?为什么有时候我们感觉脑袋里有好几个声音在吵架?为什么 “长大”似乎是一件很突然的事?这些问题,就是彼特·道格特和他的制作班底打算在《头脑特工队》里一探究竟的问题。
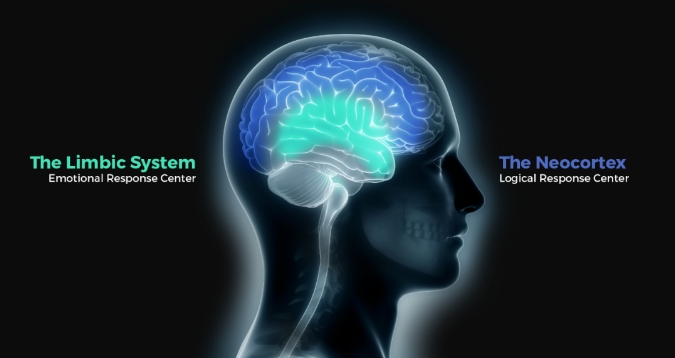
重大发现!鸟类竟然可能有自我意识?
近年来,人们发现有些鸟类的大脑也不简单,它们能制作工具、理解抽象概念,甚至能分辨莫奈和毕加索的画作。比较聪明的鸟类如猫头鹰、乌鸦、鸽子的认知能力被认为与猴子甚至类人猿相当。

如何养成新习惯,重塑大脑
改变习惯如此困难的原因不在于我们改变不了,而是因为我们对新的行为还不够熟练,坚持得不够久。万事开头难。但是一旦你对新的习惯足够熟悉了,你就有足够的力量做出改变了。以前很痛苦的事情现在对于你来说很愉快;以前需要很大决心才能完成的事现在变得很自然。
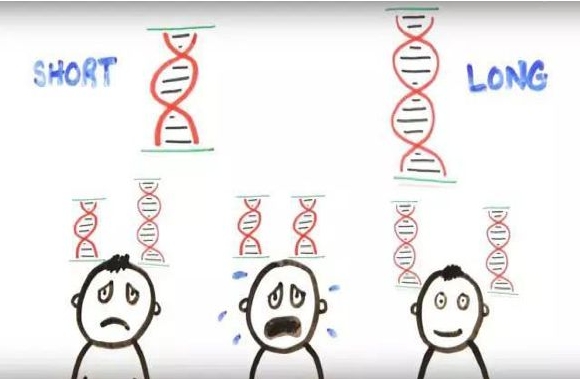
“抑郁基因”,有用还是无用?
抑郁症与某些基因有关?在过去20多年间,相关研究蓬勃开展,由此诞生了1000多篇论文。然而,不断有研究表明一些抑郁基因与精神疾病之间存在紧密关系的同时,也不断有研究证明许多呈阳性的实验结果无法重复。最近发表的一项研究更是使得“抑郁基因”遭到质疑。那么,“抑郁基因”究竟是怎样被发现的?它们在抑郁症的发病中真的具有不可忽视的重要作用吗?
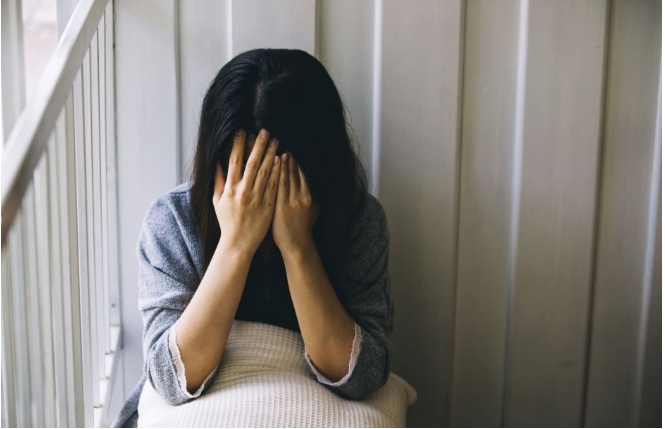

中国5400万人得抑郁症,“正能量”是压垮他们的最后一根稻草
勇敢地寻求帮助,并不是一件可耻的事情。该羞耻的不是你,是那些不了解你却肆意评判你的人。我很喜欢的一句话是,万物皆有裂痕,那是光照进来的地方。在裂痕上追逐光芒的人,不应该被嘲笑。我会给你们一个拥抱。世界和我爱着你。

国际脑科学与类脑研究回顾
人类的大脑是生物演化的奇迹,它是由数百种不同类型的上千亿的神经细胞所构成的极为复杂的生物组织。理解大脑的结构与功能是 21 世纪最具挑战性的前沿科学问题;理解认知、思维、意识和语言的神经基础,是人类认识自然与自身的终极挑战。

从美国精神卫生研究所到谷歌再出走创业, 65 岁的科学家试图革新精神疾病治疗方式
2010 年,Tom Insel 在任美国精神卫生研究所(National Institute of Mental Health,NIMH)所长的时间已经过去三分之二,该研究所是全球最大的精神卫生研究机构。他谈起精神医学及他领导的研究院如何没能帮助精神疾病患者康复,言语之坦白,非同寻常。
宁愿…也不愿意离开他?你可能患有无手机恐惧症!
发现手机快要没电?忘带手机在家?你会因为无法使用智能手机立刻感到惊慌失措或是焦虑不安吗?辗转之后,终于再次拿到手机的时候会感到如释重负、安全感爆棚吗?美国研究人员提示,你可能患有“无手机恐惧症”!
用经颅磁治疗心脑疾病,您需要注意什么?
经颅磁刺激(TMS)是一种非侵入性的大脑刺激方式,其目的是在大脑的特定区域,改变磁场及其引起的电流。由于传统抗心脑疾病药物只对40%的病患有效,且有许多的副作用,许多病人无法耐受,因此,越来越多的人已经转向经颅磁这种无痛、无创的治疗方法。TMS目前已经被临床认证,是治疗多种心脑疾病的一线治疗方法。
带您从内到外认识核磁共振(MRI)
由于个体基因和后天发展的不同,我们每个人的个体组织结构就像万花筒一样,千变万化,组成了不同而多彩的个体。您想更加了解自己组织的独特之处吗?MRI(核核共振成像)能够帮您看清身体的每一个角落!

世界冠军谷爱凌“睡得好排第一”,中国近四成失眠患者怎样才能睡一个饱觉
无法入睡、夜间早醒、多梦、睡眠呼吸暂停…据世界卫生组织(WHO)统计,全球睡眠障碍率达27%。极速发展的中国更是“睡不好”的高发区域,成年人失眠发生率高达38.2%,六成以上的90后“睡眠不足”。而这些睡眠障碍早已成为当代人在压力面前需要面对的常态。

ASMR背后的脑科学秘密--ASMR知多少
你用过疗愈声音,或“ASMR音频”来解压吗?如果没有,这篇文章能给你,进入ASMR神奇世界的一把钥匙;如果你已经体验过了ASMR,这篇硬核科普文章能一次满足你,对ASMR所有的好奇心!当你在体验ASMR 所带来的放松、快乐时,如果明白这背后的道理,也许你会更信赖ASMR,对它的反应更好。

布局元宇宙中的平行世界:从facebook改名meta说起
美东时间2021年10月28日,扎克伯格在Connect大会上正式宣布将“Facebook”更名为“Meta”——元宇宙(MetaVerse)的前缀。“Meta”源于希腊语,意为“超越”或“之上”;元宇宙,可以理解为宇宙之外的超现实世界,恰好呼应了本次大会的主题——AR与VR(增强现实与虚拟现实)。
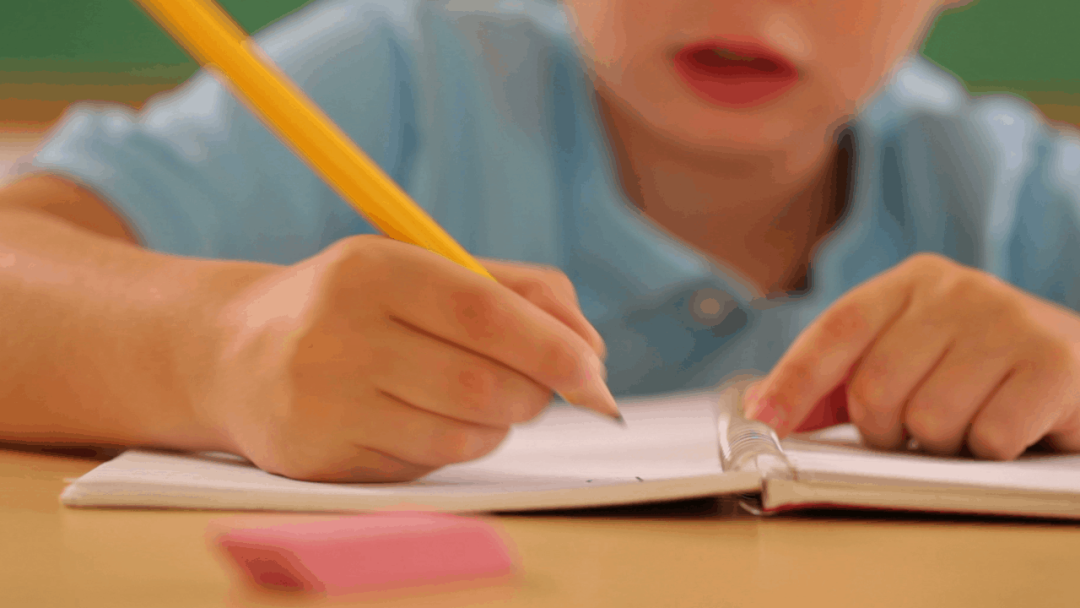

多动症ADHD的常识,读完这一篇就够了
注意力缺陷多动障碍(英语:attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,缩写为ADHD),也就是注意力缺失症、多动症(缩写为ADD),是神经发展障碍的精神症状。它的特性是难以专注、过度活跃、做事不考虑后果等等,有注意力缺失的个体也可能表现出情绪调节困难或执行功能方面的问题。虽然此病症(特别是在现代社会中)会造成一些“障碍”,但很多过动症者会对他们感兴趣或认为有价值的任务保持持续的专注,此
关于运动:我们可能有所不知
转眼盛夏,风暖蝉鸣,烈日当空。沙发土豆们,正瘫坐在空调房,只要离开片刻,便要奄奄一息。如果有灵丹妙药能够让我们才思敏捷、乐观向上、青春永驻……你要尝试一下么?什么?我们在给健身房打广告?No!也许只是一根跳绳,就能彻底改变生活哦。

老蒲的课
蒲慕明先生,祖籍广东梅州,客家人;出生于江苏南京,一岁左右随母迁往台湾;在台湾长大,台湾清华大学本科毕业之后赴美留学。后来成为美国最著名的华人教授之一,江湖人称“老蒲”。国际顶尖神经生物学家,中国科学院院士,美国国家科学院院士,中科院脑科学与智能技术卓越创新中心(原上海神经所)学术主任,是中国神经科学研究的领军人物。

游戏治愈大脑:“游戏化时代”的处方药
2020年6月15日,美国食品药品监督管理局(FDA)批准了有史以来第一款视频游戏(美国Akili Interactive公司研发的EndeavorRx)作为疾病治疗(儿童多动症,ADHD)的处方药。

正念与冥想
正念(Mindfulness),是源自佛教的一种修行方式。巴利原文是Sati,有7层含义:随念、记忆、觉察、忆起、忆持、紧系目标、不忘。正念的英文关键词是:有意识地觉察(On Purpose)、活在当下(In the Present Moment)及不做判断(Nonjudgementally)。
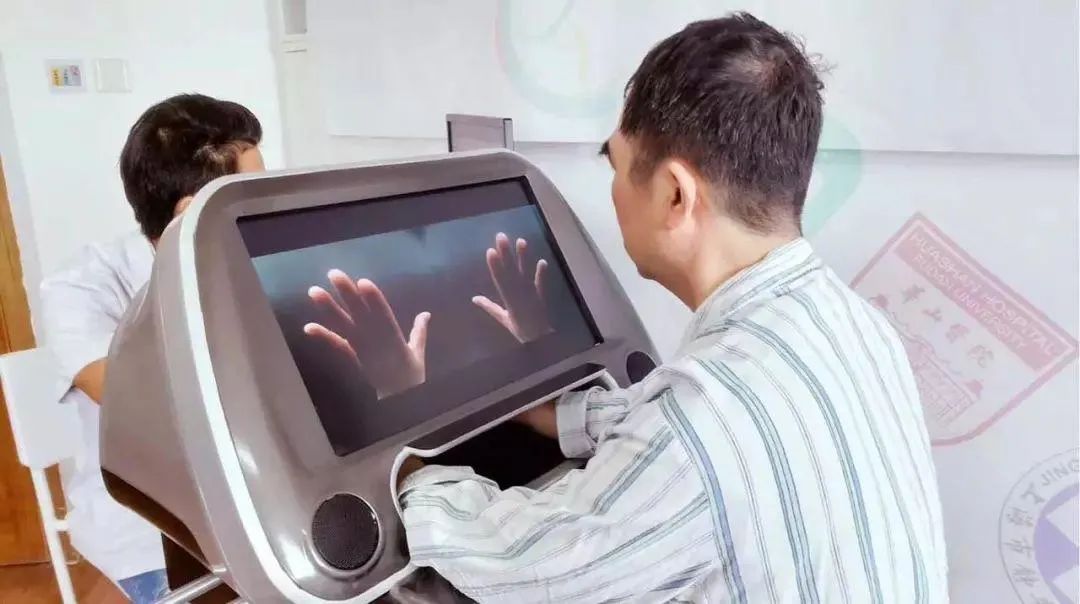

神奇的镜像疗法
镜像疗法(mirror therapy, MT)又称镜像视觉反馈疗法(mirror visual feedback, MVF)早期运用在幻肢痛患者疼痛治疗中[1],之后应用于脑卒中后的运动功能康复,对上肢功能康复特别有效。
探索数字认知疗法的奥秘
数字疗法向患者、医生及医疗服务商提供智能软件,通过临床数据、AI算法和专业医学评价指标三者的结合来衡量和干预疾病。数字疗法目前在传统疾病领域已经有一些成熟的应用,特别是针对一些慢性疾病,数字疗法可以用于追踪患者的生理指标以及监督患者的用药情况。